Periodic Table Groups Definition

These elements all line up in the eighteenth or last column of the periodic table.
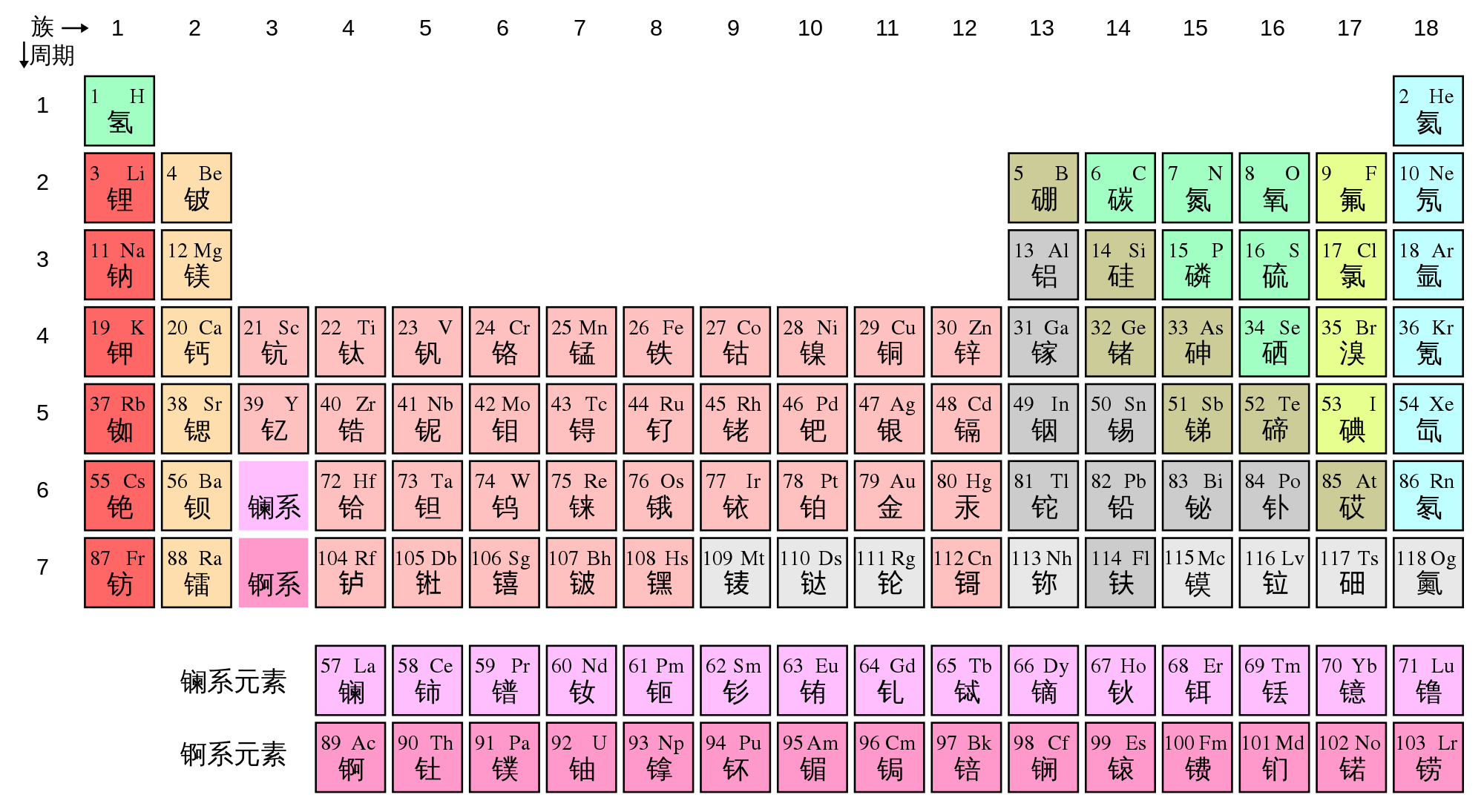
Periodic table groups definition. The periodic table is the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers. The number of each element corresponds to the number of protons in its nucleus (which is the same as the number of electrons orbiting that nucleus). Light metals these are elements of periodic table of group 1 and 2.
Periodic table, in full periodic table of the elements, in chemistry, the organized array of all the chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number—i.e., the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus. Groups are the columns of the periodic table. 18 vertical columns known as groups.
This is what is meant by periodicity or periodic table trends. The table is ‘periodic’ because elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals, i.e. The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of elements, arranges the chemical elements such as hydrogen, silicon, iron, and uranium according to their recurring properties.
7 horizontal rows known as periods. Mendeleev put elements with similar properties and that react in similar ways into the same. The figure below shows the most commonly used form of the periodic table.
Periodic table groups are columns of elements found in the modern periodic table. There are total 18 numbered groups in the modern periodic table, however, the “f” block columns between the group 2 and 3 are not numbered. One example of a group is the noble or inert gases.
Check out this free, online educational resource. A group is also known as a family of atoms in which elements are arranged within each group of the periodic table. Periods in the periodic table in each period (horizontal row), the atomic numbers increase from left […]