Dna Replication Diagram Ncert

6.1 the dna 6.2 the search for genetic material 6.3 rna world 6.4 replication 6.5 transcription 6.6 genetic code 6.7 translation 6.8 regulation of gene expression 6.9 human genome pr oject 6.10 dna fingerprinting in the previous chapter , you have lear nt the inheritance patterns and the genetic basis of such patterns.
Dna replication diagram ncert. Replication fork is an asymmetric structure, because the replication in the two arms of y is not similar. Mutations or defective dna replication. Ncert solutions for class 12 maths ncert solutions for class 12 physics ncert solutions for class 12 chemistry ncert solutions for class 12 biology ncert solutions for class 11 maths ncert.
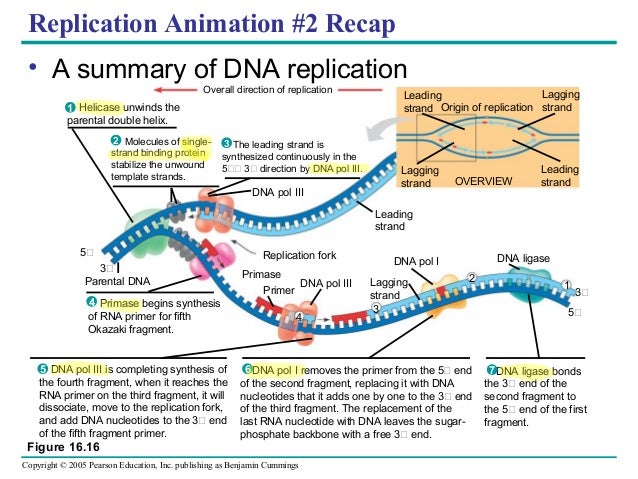
Draw a labelled diagram of a “replicating fork” showing the polarity. Watson and crick model of dna provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of double helix dna.a dna is a polymer which is composed by the combination of several monomer units refers as “deoxyribo nucleotides” linked by the phosphodiester bond.in the discovery of dna, many scientists have explicated the structure of dna, its components and composition etc. In the given flow diagram, the*replication of retrovirus in a host is shown.
There can be dna replication without cell division. These two strands are easily separable because the hydrogen bonds which hold […] <br> this creates some additional complications at the replicating fork.
Draw a labeled schematic sketch of replication fork of dna. (c) can the infected cell survive while viruses are being replicated and released ? (a) differences between pollination and fertilization
(a) draw a labelled diagram of a replicating fork showing the polarity. The entire process of dna replication can be discussed under many steps. Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid which is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live and reproduce.;
In eukaryotes, there are multiple origin of replication present. Dna replication is an important process that occurs during cell division. Ars (autonomously replicating sequence) in case of yeast is origin for replication.